Highly Effective Antibacterial Vesicles Based on Peptide-Mimetic Alternating Copolymers for Bone Repair
作者:Zhou, C. C.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, P. Y.; Wang, F. Y. K.; Hong, Y. X.; Wang, N. S.; Xu, S. G.*; Du, J. Z.* 时间:2017-10-11 点击数:
Abstract:
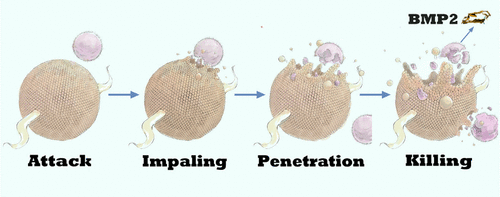
It is an important challengefor bone repair to effectively deliver growth factors and at the same time to prevent and cure inflammation without obvious pathogen resistance. We designed a kind of antibacterial peptide-mimetic alternating copolymers (PMACs) to effectively inhibit and kill both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The minimum inhibition concentrations (MICs) of the PMACs against E. coli and S. aureus are 8.0 μg/mL, which are much lower than that of antibacterial peptides synthesized by other methods such as widely used ring-opening polymerization of N-carboxyanhydride. Furthermore, the PMACs can self-assemble into polymer vesicles (polymersomes) in pure water with low cytotoxicity (IC50 > 1000 μg/mL), which can encapsulate growth factors in aqueous solution and release them during long-term antibacterial process for facilitating bone repair. We also find that the alternating structure is essential for the excellent antibacterial activity. The in vivo tests in rabbits confirmed that the growth-factor-encapsulated antibacterial vesicles have better bone repair ability compared with control groups without antibacterial vesicles. Overall, we have provided a novel method for designing PMAC-based highly effective intrinsically antibacterial vesicles that may have promising biomedical applications in the future.
文章链接:Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 4154–4162.