Antibacterial hydrogels incorporated with poly(glutamic acid)-based vesicles
作者:Song, T.; Xi, Y. J.; Du, J. Z.* 时间:2017-09-13 点击数:
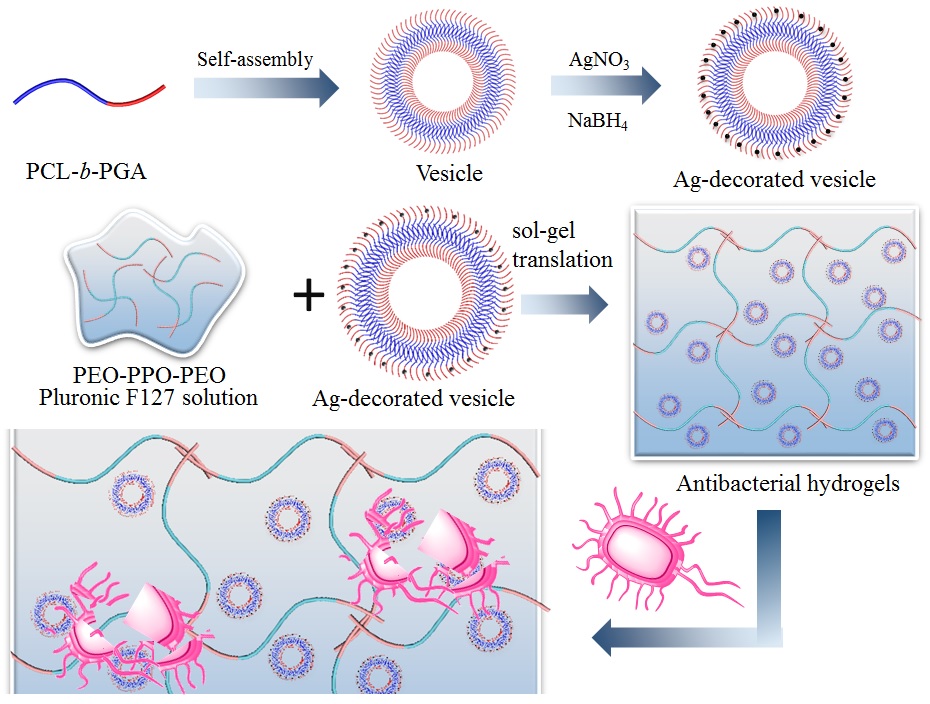
Abstract:
Antibacterial hydrogels with durable and efficient antibacterial ability are promising biomedical materials. Copolymers with poly(amino acid) segments may provide unique functionalities for hydrogels. Herein, polycaprolactone-block-poly(glutamic acid) (PCL-b-PGA) was synthesized by ring-opening polymerization (ROP) and subsequently self-assembled into vesicles. Furthermore, antibacterial Ag-decorated vesicles were prepared by in situ deposition of silver nanoparticles in the carboxyl groups on the PGA coronas of vesicles. Meanwhile, the Ag-decorated vesicles were incoporated into Pluronic F127 hydrogels to afford antibacterial hydrogels. The MIC90 (minimum concentration of inhibiting 90% of bacterium) of antibacterial vesicles against Gram-negative bacterium E. coli and Gram-positive bacterium S. aureus are 10 μg mL-1 and 20 μg mL-1, which afford the hydrogels excellent antibacterial property. Oxford cup tests confirmed that the MIC50 against both E. coli and S. aureus is 7.5 μg mL-1 and the MBC (minimum concentration of inhibiting 100% of bacterium) against either of them is 30 μg mL-1. Overall, we provide a new method for preparing antibacterial hydrogels for long-acting biomedical applications.
文章链接:Acta Polymerica Sinica 2017, Accepted.