Preparation of water-dispersible silver-decorated polymer vesicles and micelles with excellent antibacterial efficacy
作者:Hang Lu,Lang Fan,Qiuming Liu,Jingren Wei,Tianbin Rena,Jianzhong Du 时间:2012-05-01 点击数:
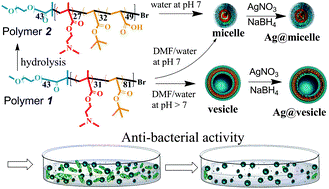
Abstract
It is well known that
silver nanoparticles
have excellent antibacterial activities. However, to prepare well-defined, water-dispersible and long-term stable
silver nanoparticles
still remains insufficient. Presented in this paper are the design and preparation of new water-dispersible silver-decorated
polymer
vesicles and micelles based on a new kind of amphiphilic block-
statistical
copolymer
, PEO-b-P(DMA-stat-tBA) (
polymer
1) and its partially hydrolyzed derivative, PEO-b-P(DMA-stat-tBA-stat-AA) (
polymer
2). Here PEO stands for poly(ethylene oxide), DMA for
2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate
, tBA for
t
-butyl acrylate
and AA for
acrylic acid
. PEO and poly(tBA) are designed to provide permanent hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity for macromolecular
self-assembly
in
water
, respectively. Poly(DMA) is introduced for the coordination of Ag+ ions to form
silver nanoparticles
in situ upon
reduction
. Poly(AA) is designed to serve the scaffold for the
silver nanoparticle
formation in the micelle core by electrostatic interactions with Ag+ ions. The silver-decorated
polymer
vesicles and micelles have been prepared in five steps: Firstly,
polymer
1 was synthesized by Atom Transfer
Radical Polymerization
(
ATRP
) in the presence of CuBr/PMDETA in
methanol
at 60 °C. Secondly, a fraction of hydrophobic poly(tBA) in
polymer
1 was hydrolyzed into hydrophilic and functional poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) to form
polymer
2 in the presence of
trifluoroacetic acid
(TFA). Thirdly,
polymer
1 was self-assembled into
polymer
vesicles with tuneable sizes ranged from 100–700 nm in basic
water
–DMF and
polymer
micelles with ∼50 nm diameter in neutral
water
–DMF, respectively.
Polymer
2 was self-assembled into small micelles with ∼20 nm diameter by direct dissolution in
water
. Fourthly, the silver precursor AgNO3 was introduced into the
polymer
micelle or
polymer
vesicle solution where the Ag+ ion was absorbed in the core of the micelles or the membrane of the vesicles. Finally, the Ag
nanoparticles
were formed in the core of the micelles or the membrane of the vesicles when the
reducing agent
sodium borohydride
was introduced.
1
H NMR
,
GPC
,
DLS
, UV and
TEM
were employed to characterize the structure and composition of the
block copolymers
,
polymer
micelles and vesicles, and silver-decorated
polymer
micelles and vesicles. Those water-dispersible silver-decorated
polymer
micelles and vesicles showed excellent antibacterial efficacy against Escherichia coli (E. coli) with quite low minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC).
文章链接:Polymer Chemistry 2012, 3, 2217-2227.