Antibacterial high-genus polymer vesicle as an “armed” drug carrier
作者:Hongshi Zhu, Qingrui Geng, Wenqin Chen, Yunqing Zhu, Jing Chen and Jianzhong Du 时间:2013-08-06 点击数:
Abstract
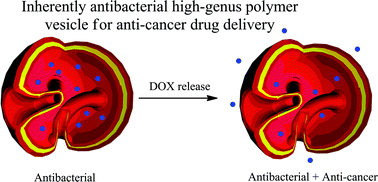
Presented in this paper is an “armed” high-genus block copolymer vesicle (g = 18) which has excellent blood compatibility and more internal barriers than simple polymer vesicles (g = 0) for controlled anti-cancer drug delivery. The high-genus vesicle also shows better antibacterial activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria without quaternary ammonium moieties or the loading of any external antibiotics compared to the non-self-assembled individual polymer chains, or a conventional simple vesicle. This high-genus polymer vesicle was prepared by the self-assembly of PMEO2MA20-b-PTA20 diblock copolymers in DMF–water, where PMEO2MA is thermo-responsive poly[2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethyl methacrylate] and PTA is pH-responsive and antibacterial poly[2-(tert-butylaminoethyl) methacrylate]. Doxorubicin (DOX) loading/release experiments revealed a retarded release rate of DOX in high-genus block copolymer vesicles than conventional simple vesicles, which could be used as an efficient drug delivery carrier with more internal barriers for drug molecules than conventional simple vesicles. Moreover, this “armed” drug delivery vehicle makes antibacterial and anti-cancer therapeutic processes proceed spontaneously, representing a safer and more efficient drug delivery system in nanomedicine.
文章链接:Journal of Materials Chemistry B 2013, 1, 5496-5504.